#!/bin/bash
declare -A USE_MAP
declare -a ENABLES
# export_name dependency dependecy dependency...
USE_MAP['HBASE']='USE_HBASE HCATALOG HUE'
USE_MAP['PIG']='USE_PIG'
USE_MAP['HUE']='USE_HUE'
USE_MAP['HCATALOG']='USE_HCATALOG'
USE_MAP['PRESTO']='USE_PRESTO HCATALOG'
ENABLES=()
function use() {
local dep=(${USE_MAP["$1"]})
ENABLES+=(${dep[0]})
dep=("${dep[@]:1}")
if [ ! -z "$dep" ]; then
for item in ${dep[@]}; do
use $item
done
fi
}
function export_enabled() {
sorted_use=($(echo "${ENABLES[@]}" | tr ' ' '\n' | sort -u | tr '\n' ' '))
for item in ${sorted_use[@]}; do
echo "export $item";
done
}
use HBASE
export_enabled
------
$ bash resolve.sh
export USE_HBASE
export USE_HCATALOG
export USE_HUECategory: unix
Ambari – user can log in but has no privileges
We ran into some interesting issue – user has all the privileges, was in correct ldap group, can log in to the ambari, but privileges weren’t effective.
I did multiple discoveries – checked log ambari-server.log and found out following
com.google.common.cache.CacheLoader$InvalidCacheLoadException: CacheLoader returned null for key myuser.So, tried to restart ambari-server, didn’t work. Did further investigation, using ambari API
$ curl -XGET -H"X-Requested-By: ambari" -u admin:... https://ambari.mycluster.com/api/v1/users/myuser
{
"href" : "http://ambari.mycluster.com/api/v1/users/myuser",
"Users" : {
"active" : true,
"admin" : false,
"groups" : [
"ldap-users",
"cluster-admins"
],
"ldap_user" : false,
"user_name" : "MYUSER",
"user_type" : "PAM"
},so, this worked. Notice uppercase in user_name. So I tried to fetch user info with privileges
$ curl -XGET -H"X-Requested-By: ambari" -u admin:... https://ambari.mycluster.com/api/v1/users/myuser?fields=privileges/*
{
"href" : "http://ambari.mycluster.com/api/v1/users/myuser?fields=privileges/*",
"Users" : {
"user_name" : "MYUSER"
},
"privileges" : [
{
"href" : "http://ambari.mycluster.com/api/v1/users/myuser/privileges/153",
"PrivilegeInfo" : {
"instance_name" : "INSTANCE",
"permission_label" : "View User",
"permission_name" : "VIEW.USER",
"principal_name" : "cluster-admins",
"principal_type" : "GROUP",
"privilege_id" : 153,
"type" : "VIEW",
"user_name" : "MYUSER",
"version" : "2.4.3.0",
"view_name" : "ADMIN_VIEW"
}
},Nice. Works too. So another check – load only certain privileges – 153.
$ curl -XGET -H"X-Requested-By: ambari" -u admin:... https://ambari.mycluster.com/api/v1/users/myuser/privileges/153
{
"status": 500,
"message": "Server Error"
}
and even upcase
$ curl -XGET -H"X-Requested-By: ambari" -u admin:... https://ambari.mycluster.com/api/v1/users/MYUSER/privileges/153
{
"status": 500,
"message": "Server Error"
}Aha! Looks like there’s some inconsitency in the postgres database. So, check it!
ambari=> select * from users where user_name='myuser';
user_id | principal_id | ldap_user | user_name | create_time | user_password | active | active_widget_layouts | user_type
---------+--------------+-----------+-----------+-------------+---------------+--------+-----------------------+-----------
(0 rows)
ambari=> select * from users where user_name='MYUSER';
user_id | principal_id | ldap_user | user_name | create_time | user_password | active | active_widget_layouts | user_type
---------+--------------+-----------+-----------+------------------------+---------------+--------+-----------------------+-----------
16005 | 20005 | 0 | MYUSER | 2019-11-22 04:37:44.18 | | 1 | [{"id":"29405"}] | PAM
(1 row)Gotcha. There’s no such user named myuser in the database – and pg is case sensitive. So, rename the user
ambari=> update users set user_name='myuser' where user_id=16005;
UPDATE 1
ambari=> \qand restart ambari-server. Now we can try again the api call
$ curl -XGET -H"X-Requested-By: ambari" -u admin:... https://ambari.mycluster.com/api/v1/users/myuser/privileges/153
{
"href" : "http://ambari.mycluster.com/api/v1/users/myuser/privileges/153",
"PrivilegeInfo" : {
"instance_name" : "INSTANCE",
"permission_label" : "View User",
"permission_name" : "VIEW.USER",
"principal_name" : "cluster-admins",
"principal_type" : "GROUP",
"privilege_id" : 153,
"type" : "VIEW",
"user_name" : "myuser",
"version" : "2.4.3.0",
"view_name" : "ADMIN_VIEW"
}
}Voila!
Side by side images
Quick script. As I’ve got FLIR images of my house, I wanted to have them side by side – original image + FLIR. So I wrote some small (fast) script in bash to do that.
#!/bin/bash
ir=IR_
img=DC_
im_start=$1
ir_start=$((im_start-1))
echo "Starting from $start - $(printf "%s%04d.jpg" $img $im_start)"
echo "IR will be from $ir_start - $(printf "%s%04d.jpg" $ir $ir_start)"
if [[ ! -f "$(printf "%s%04d.jpg" $img $im_start)" ]]; then
echo "Image doesn't exist!"
exit
fi
if [[ ! -f "$(printf "%s%04d.jpg" $ir $ir_start)" ]]; then
echo "IR doesn't exist!"
exit
fi
loop=1
while [ $loop -ne 0 ];do
image=$(printf "%s%04d.jpg" $img $im_start)
ir_image=$(printf "%s%04d.jpg" $ir $ir_start)
combined_image=$(printf "flir-%04d-%04d.jpg" $im_start $ir_start)
echo -n "$image + $ir_image --> $combined"
montage -mode concatenate -tile x1 $image $ir_image $combined_image
echo "..Done!"
# increase
im_start=$((im_start+2))
ir_start=$((ir_start+2))
#echo "Next file $(printf "%s%04d.jpg" $img $im_start)"
# test if file?
if [[ ! -f "$(printf "%s%04d.jpg" $img $im_start)" ]]; then
loop=0
fi
done
And the resulting image:
sidekiq getting stuck?
We had quite strange scenario. Two hosts with sidekiq, one working well, second one gets stuck after few seconds or minutes. Happened in workers with opening new TCP/UDP connections. So, I started to review all the files, where ‘max files’ is set.
$ cat /etc/security/limits.conf * soft nofile 30000 * hard nofile 60000 tom@web:~$ ulimit -Hn 60000 tom@web:~$ ulimit -Sn 30000 tom@web:~$ /sbin/sysctl -a | grep "file-max" fs.file-max = 60000
So, all this looks OK so far. After numerous checks I’ve found, that our eye process is running for a while, maybe since the beginning and probably it took old file-max settings. How to check? Simply run eye info or get PID of the sidekiq process and run following command (assume 22613 is the PID):
tom@web:~$ cat /proc/22613/limits Limit Soft Limit Hard Limit Units Max cpu time unlimited unlimited seconds Max file size unlimited unlimited bytes Max data size unlimited unlimited bytes Max stack size 8388608 unlimited bytes Max core file size 0 unlimited bytes Max resident set unlimited unlimited bytes Max processes 516140 516140 processes Max open files 1024 4096 files Max locked memory 65536 65536 bytes Max address space unlimited unlimited bytes Max file locks unlimited unlimited locks Max pending signals 516140 516140 signals Max msgqueue size 819200 819200 bytes Max nice priority 0 0 Max realtime priority 0 0 Max realtime timeout unlimited unlimited us
Gotcha! 1024 as soft-limit, 4096 hard limit. The fix is pretty simple – just quit eye , load it’s config and restart sidekiq.
tom@web:~$ eye quit quit... tom@web:~$ eye load config.eye eye started! config loaded! tom@web~$ eye restart sidekiq tom@web:~$ cat /proc/4624/limits Limit Soft Limit Hard Limit Units Max cpu time unlimited unlimited seconds Max file size unlimited unlimited bytes Max data size unlimited unlimited bytes Max stack size 8388608 unlimited bytes Max core file size 0 unlimited bytes Max resident set unlimited unlimited bytes Max processes 516140 516140 processes Max open files 30000 60000 files Max locked memory 65536 65536 bytes Max address space unlimited unlimited bytes Max file locks unlimited unlimited locks Max pending signals 516140 516140 signals Max msgqueue size 819200 819200 bytes Max nice priority 0 0 Max realtime priority 0 0 Max realtime timeout unlimited unlimited us
voila! We’re back on track :)
sendmail + osx 10.10.4/ios 8.4/ios 9
After upgrade I was unable se to send mails through my sendmail, from both OSX 10.10.4 and upgraded iOS9 …
this was in my sendmail log:
Jul 12 19:58:03 orin sendmail[12164]: STARTTLS=server, error: accept failed=0, SSL_error=1, errno=0, retry=-1 Jul 12 19:58:03 orin sendmail[12164]: STARTTLS=server: 12164:error:14094410:SSL routines:SSL3_READ_BYTES:sslv3 alert handsh ake failure:s3_pkt.c:1053:SSL alert number 40
fix is amazingly easy and effective:
generate dh2048 certificate:
openssl gendh -out dh_2048.pem -2 2048
and add to sendmail.mc:
define(`confDH_PARAMETERS',`/etc/mail/certs/dh_2048.pem')
then recompile your .mc and restart sendmail.
Optimizing fluentd
We’re currently using (for one part of our infrastructure) logging into elasticsearch. We have fluentd collectors and kibana interface for viewing and searching through the logs. 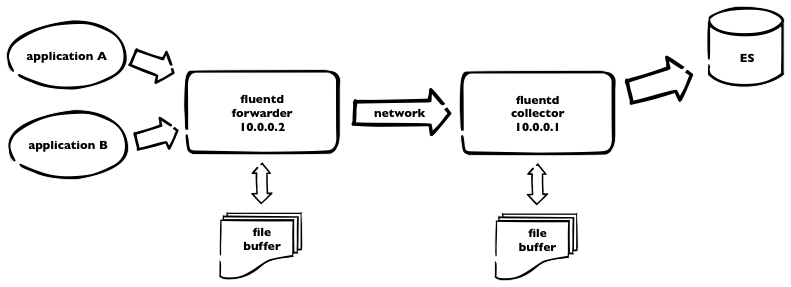 This is how it works. Logs are sent to fluentd forwarder and then over the network to fluentd collector, which pushes all the logs to elasticsearch. As we have plenty of logs, we need to incorporate some buffering – on both sides – using buffer_file statement in the fluentd config. Here is a part of our fluentd config from forwarder
This is how it works. Logs are sent to fluentd forwarder and then over the network to fluentd collector, which pushes all the logs to elasticsearch. As we have plenty of logs, we need to incorporate some buffering – on both sides – using buffer_file statement in the fluentd config. Here is a part of our fluentd config from forwarder
<match ***>
type forward
send_timeout 60s
recover_wait 10s
heartbeat_interval 1s
phi_threshold 16
hard_timeout 120s
# buffer
buffer_type file
buffer_path /opt/fluentd/buffer/
buffer_chunk_limit 8m
buffer_queue_limit 4096
flush_interval 10s
retry_wait 20s
# log to es
<server>
host 10.0.0.1
</server>
<secondary>
type file
path /opt/fluentd/failed/
</secondary>
</match>
and the same for the collector
<source> type forward bind 10.0.0.1 </source> <match log.**> type elasticsearch logstash_format true # elastic host host 10.0.0.3 port 9200 logstash_prefix log include_tag_key # buffering buffer_type file buffer_path /opt/fluentd/buffer/ flush_interval 5m buffer_chunk_limit 16m buffer_queue_limit 4096 retry_wait 15s </match>
So. For the forwarder, we’re using buffer with max 4096 8MB chunks = 32GB of buffer space. Forwarder is flushing every 10secs. For collector, we use bigger chunks, as elasticsearch is capable to handle it – but not using default 256MB chunks due to memory limitations. Flushing period is longer – and should be – recommended value is 5minutes. We can keep up to 64Gigs of buffer data.
What happens if one of the fluentd dies. Some data will be probably lost, when unsaved to buffer. But. When there’s connection lost or collector fluentd isn’t running, all logs, collected by forwarder, are stored into the buffer – and sent later. Which is great. The same when ES is down for some reason, collector node is still receiving data and is able to continue sending into ES after full recovery.
PS: don’t forget to make some tweaks to the system itself, like raise the limit for max files opened and some tcp tunning.
Securing kibana + elasticsearch
After some successful setup of Kibana + es for fluentd there’s a need to secure whole website. So I decided to use nginx and basic auth. I assume you have standard configuration – with es running on localhost:9200.
# htpasswd -c /opt/nginx/conf/.htpasswd some_user
and now modify nginx config:
#user nobody;
#group nogroup;
worker_processes 5;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
'$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
'"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
sendfile on;
keepalive_timeout 65;
gzip on;
server {
# we listen on :8080
listen 8080;
server_name somer.server;
charset utf-8;
access_log logs/host.access.log main;
# root for Kibana installation
location / {
auth_basic "Restricted";
auth_basic_user_file /opt/nginx/conf/.htpasswd;
root /opt/kibana;
index index.html index.htm;
}
# and for elasticsearch
location /es {
auth_basic "Restricted - ES";
auth_basic_user_file /opt/nginx/conf/.htpasswd;
rewrite ^/es/_aliases$ /_aliases break;
rewrite ^/es/_nodes$ /_nodes break;
rewrite ^/es/(.*/_search)$ /$1 break;
rewrite ^/es/(.*/_mapping)$ /$1 break;
rewrite ^/es/(.*/_aliases)$ /$1 break;
rewrite ^/es/(kibana-int/.*)$ /$1 break;
return 403;
# set some headers
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header Host $http_host;
proxy_pass http://localhost:9200;
}
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
}
}
Duplicity – BackendException: ssh connection to server:22 failed: Unknown server
Booom! After reinstall of one of our servers I got into this. Weird error. It’s caused by paramiko. There’s no code fix available, but reason is simple – and fix too.
Connect to your box, and simply remove two files from /etc/ssh directory
root@limone:/# ls -la /etc/ssh/ total 168 drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Apr 24 15:31 . drwxr-xr-x 82 root root 4096 Apr 24 16:00 .. -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 136156 Feb 8 2013 moduli -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 1669 Feb 8 2013 ssh_config -rw------- 1 root root 668 Apr 23 12:05 ssh_host_dsa_key -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 601 Apr 23 12:05 ssh_host_dsa_key.pub -rw------- 1 root root 227 Apr 23 12:05 ssh_host_ecdsa_key -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 173 Apr 23 12:05 ssh_host_ecdsa_key.pub -rw------- 1 root root 1675 Apr 23 12:05 ssh_host_rsa_key -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 393 Apr 23 12:05 ssh_host_rsa_key.pub -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 2510 Apr 23 12:15 sshd_config
so, remove these two files:
-rw------- 1 root root 227 Apr 23 12:05 ssh_host_ecdsa_key -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 173 Apr 23 12:05 ssh_host_ecdsa_key.pub
Then clean up ~/.ssh/known_hosts file on the box your’re running backup from
ssh-keygen -f "/root/.ssh/known_hosts" -R server_fqdn ssh-keygen -f "/root/.ssh/known_hosts" -R server_ip
connect using ssh to backup server from that host (to write id_rsa keys into known_hosts file)
# ssh root@server_fqdn Warning: the RSA host key for 'server_fqdn' differs from the key for the IP address 'server_ip' Offending key for IP in /root/.ssh/known_hosts:3 Matching host key in /root/.ssh/known_hosts:11 Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? yes root@server_fqdn's password:
and run duplicate again.
voila! :)
redis sentinel setup
Prerequisities
- multiple clients with redis 2.8.2+ installed
Do I need sentinel? If you want to have some kind of redis failover (there’s no cluster yet) – yes. Sentinels continuously monitor every redis instance and change configuration of given redis node(s) – if specified number of sentinels decided whether master is down, then they elect and promote new master and set other nodes as a slave of this master.
Looks interesting? Yes. It is. But. There’s a little time gap between electing and switching to the new master. You have to resolve this on application level.
Basically. Initial setup expects all nodes running as a master, with manual set slaveof ip port in redis-cli on meaned redis slaves. Then run sentinel and it does the rest.
sample redis configururation files follow:
daemonize yes pidfile /usr/local/var/run/redis-master.pid port 6379 bind 10.0.0.1 timeout 0 loglevel notice logfile /opt/redis/redis.log databases 1 save 900 1 save 300 10 save 60 10000 stop-writes-on-bgsave-error yes rdbcompression yes rdbchecksum yes dbfilename master.rdb dir /usr/local/var/db/redis/ slave-serve-stale-data yes slave-read-only no slave-priority 100 maxclients 2048 maxmemory 256mb # act as binary log with transactions appendonly yes appendfsync everysec no-appendfsync-on-rewrite no auto-aof-rewrite-percentage 100 auto-aof-rewrite-min-size 64mb lua-time-limit 5000 slowlog-log-slower-than 10000 slowlog-max-len 128 hash-max-ziplist-entries 512 hash-max-ziplist-value 64 list-max-ziplist-entries 512 list-max-ziplist-value 64 set-max-intset-entries 512 zset-max-ziplist-entries 128 zset-max-ziplist-value 64 activerehashing yes client-output-buffer-limit normal 0 0 0 client-output-buffer-limit slave 256mb 64mb 60 client-output-buffer-limit pubsub 32mb 8mb 60
and sentinel configuration file:
port 17700 daemonize yes logfile "/opt/redis/sentinel.log" sentinel monitor master 10.0.0.1 6379 2 sentinel down-after-milliseconds master 4000 sentinel failover-timeout master 180000 sentinel parallel-syncs master 4
Start all of your redis nodes with redis config and choose master. Then run redis console and set all other nodes as a slave of given master, using command slaveof 10.0.0.1 6379. Then you can connect to your master and verify, if there are all of your slave nodes, connected and syncing – run info command in your master redis console. Output should show you something like this
- snip - # Replication role:master connected_slaves:3 slave0:ip=10.0.0.2,port=6379,state=online,offset=17367254333,lag=1 slave1:ip=10.0.0.3,port=6379,state=online,offset=17367242971,lag=1 slave2:ip=10.0.0.4,port=6379,state=online,offset=17367222381,lag=1 - snip-
To test, if your sentinel works, just shutdown your redis master and watch sentinel log. You should see something like this
[17240] 04 Dec 07:56:16.289 # +sdown master master 10.24.37.144 6379 [17240] 04 Dec 07:56:16.551 # +new-epoch 1386165365 [17240] 04 Dec 07:56:16.551 # +vote-for-leader 185301a20bdfdf1d5316f95bae0fe1eb544edc58 1386165365 [17240] 04 Dec 07:56:17.442 # +odown master master 10.0.0.1 6379 #quorum 4/2 [17240] 04 Dec 07:56:18.489 # +switch-master master 10.0.0.1 6379 10.0.0.2 6379 [17240] 04 Dec 07:56:18.489 * +slave slave 10.0.0.3:6379 10.0.0.3 6379 @ master 10.0.0.2 6379 [17240] 04 Dec 07:56:18.490 * +slave slave 10.0.0.4:6379 10.0.0.4 6379 @ master 10.0.0.2 6379 [17240] 04 Dec 07:56:28.680 * +convert-to-slave slave 10.0.0.1:6379 10.0.0.1 6379 @ master 10.0.0.2 6379
explained line by line
+sdown master master 10.24.37.144 6379
master is subjectively down (maybe)
+odown master master 10.0.0.1 6379 #quorum 4/2
master is objectively down (oh, really), two of four sentinels have the same opinion
+switch-master master 10.0.0.1 6379 10.0.0.2 6379
so we switch to another master – chosen 10.0.0.2
+slave slave 10.0.0.3:6379 10.0.0.3 6379 @ master 10.0.0.2 6379
reconfigure 10.0.0.3 as a slave of new master 10.0.0.2
+convert-to-slave slave 10.0.0.1:6379 10.0.0.1 6379 @ master 10.0.0.2 6379
sorry, former master, you have to serve as a slave now
+sdown, -odown? + means ‘is’, – means ‘is no longer’. Then “+sdown” can be translated as “is subjectively down” and “-odown” like “is no longer objectively down”. Simple, huh? :)
PS: take my configuration files as a sample. Feel free to modify to match your need and check redis/sentinel configuration docs to get deeper knowledge about configuration options.
rails + passenger + nginx maintenance mode
I need to add maintenance page to some rails app, running with passenger and nginx. Here’s some config and steps.
You just need to add static html file to app_root/public/maintenance.html – and I assume css files on /assets url.
so, here’s nginx config:
server {
listen 80;
server_name = www.example.com;
root /home/deploy/www.example.com/public;
passenger_enabled on;
passenger_min_instances 5;
set $maintenance 0;
# is there maintenance file set?
if (-f $document_root/../tmp/maintenance.txt) {
set $maintenance 1;
}
# exclude /assets
if ( $uri ~* ^/assets\/\.* ) {
set $maintenance 0;
}
# in maintenance mode - send 503 status
if ($maintenance = 1) {
return 503;
}
# maintenance mode
error_page 503 @503;
# rewrite everything to maintenance.html
location @503 {
rewrite ^ /maintenance.html last;
break;
}
}
setting maintance mode is really simple – set app_root/tmp/maintenance.txt file – when escaping, just remove that file.
