#!/bin/bash
declare -A USE_MAP
declare -a ENABLES
# export_name dependency dependecy dependency...
USE_MAP['HBASE']='USE_HBASE HCATALOG HUE'
USE_MAP['PIG']='USE_PIG'
USE_MAP['HUE']='USE_HUE'
USE_MAP['HCATALOG']='USE_HCATALOG'
USE_MAP['PRESTO']='USE_PRESTO HCATALOG'
ENABLES=()
function use() {
local dep=(${USE_MAP["$1"]})
ENABLES+=(${dep[0]})
dep=("${dep[@]:1}")
if [ ! -z "$dep" ]; then
for item in ${dep[@]}; do
use $item
done
fi
}
function export_enabled() {
sorted_use=($(echo "${ENABLES[@]}" | tr ' ' '\n' | sort -u | tr '\n' ' '))
for item in ${sorted_use[@]}; do
echo "export $item";
done
}
use HBASE
export_enabled
------
$ bash resolve.sh
export USE_HBASE
export USE_HCATALOG
export USE_HUECategory: programming
R – Četnost podruhé
Mějme následující data:
> head(dotaznik.csv[,c(2,3)]) type gender 1 H F 2 H M 3 A F 4 A M 5 A F 6 H M
A potřebujeme zjistit absolutní a relativní četnost výskytu žen a mužů, rozdělenou ještě podle hodnoty v type .
> tbl <- table(dotaznik.csv$gender, dotaznik.csv$type)
> tbl
A H
M 18 16
Ž 17 19
Opět převedeme na data frame
> tbl.frame <- as.data.frame(tbl) > tbl.frame Var1 Var2 Freq 1 M A 18 2 Ž A 17 3 M H 16 4 Ž H 19
A máme absolutní četnost. Teď vypočítáme relativní četnost.
> library(plyr) > ddply(tbl.frame, .(Var2), transform, prop=Freq/sum(Freq)) Var1 Var2 Freq prop 1 M A 18 0.5142857 2 Ž A 17 0.4857143 3 M H 16 0.4571429 4 Ž H 19 0.5428571
Což znamená: pro každý subset z framu tbl.frame , rozdělený podle proměnné Var2 , proveď transform , a vypočti relativní četnost podle frekvence (abs. četnosti) a součtu hodnot frekvence.
R – četnost a graf
Dostal jsem pověření z nejvyšších míst vyrobit statistické zhodnocení dotazníků. A protože bytostně nemám rád Excel, našel jsem R a zkouším.
Udělal jsem data do CSV souboru a nahrál do R (RStudio)
> head(dotaznik.csv) num type gender age height weight edu 1 1 H M 60 182 100 Vysokoškolské 2 2 H M 49 188 102 Vyučen/a 3 3 H M 61 176 75 Vyučen/a 4 4 H M 56 180 110 Střední 5 5 H M 47 180 95 Vysokoškolské 6 6 H M 48 178 95 Střední
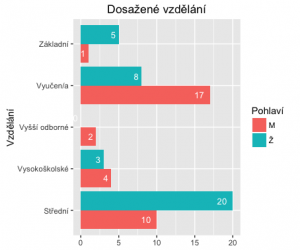
Zkusíme vyrobit četnost vzdělání (edu) a potom ji ještě rozdělit podle pohlaví (gender).
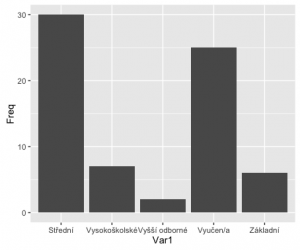
> edu <- table(dotaznik.csv$edu)
> edu
Střední Vysokoškolské Vyšší odborné Vyučen/a
30 7 2 25
Základní
6
Máme tabulku, ale potřebujeme z ní frame
> fedu <- as.data.frame(edu)
> fedu
Var1 Freq
1 Střední 30
2 Vysokoškolské 7
3 Vyšší odborné 2
4 Vyučen/a 25
5 Základní 6
Přidáme relativní četnost (mean)
> fedu$mean <- fedu$Freq / sum(fedu$Freq)
> fedu
Var1 Freq mean
1 Střední 30 0.42857143
2 Vysokoškolské 7 0.10000000
3 Vyšší odborné 2 0.02857143
4 Vyučen/a 25 0.35714286
5 Základní 6 0.08571429
A teď na graf. Používáme ggplot2.
ggplot(fedu, aes(x=Var1, y=Freq)) + geom_bar(stat='identity')
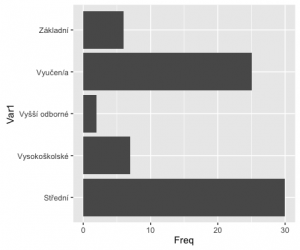
Fajn. Ale chceme graf otočit
ggplot(fedu, aes(x=Var1, y=Freq)) + geom_bar(stat='identity') + coord_flip()
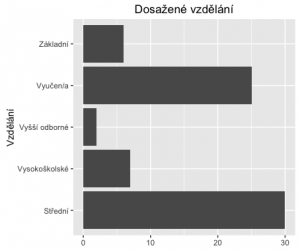
Teď ještě smazat popisek osy x a přepsat osu y.
ggplot(fedu, aes(x=Var1, y=Freq)) + geom_bar(stat='identity') +
coord_flip() +
xlab('Vzdělání') +
theme(axis.title.x = element_blank()) +
ggtitle('Dosažené vzdělání')
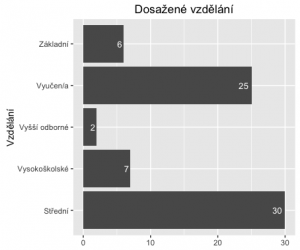
A finálně přidáme hodnoty frekvence do jednotlivých sloupců.
ggplot(fedu, aes(x=Var1, y=Freq)) +
geom_bar(stat='identity', position=position_dodge()) +
geom_text(aes(label=Freq), hjust=1.3, color="white",position = position_dodge(0.9), size=3.5) +
coord_flip() +
xlab('Vzdělání') +
theme(axis.title.x = element_blank()) +
ggtitle('Dosažené vzdělání')
A teď trochu komplexněji. Ještě to rozdělíme na muže a ženy..
> edu <- table(dotaznik.csv$gender, dotaznik.csv$edu)
> edu
Střední Vysokoškolské Vyšší odborné Vyučen/a Základní
M 10 4 2 17 1
Ž 20 3 0 8 5
> fedu <- as.data.frame(edu)
> fedu
Var1 Var2 Freq
1 M Střední 10
2 Ž Střední 20
3 M Vysokoškolské 4
4 Ž Vysokoškolské 3
5 M Vyšší odborné 2
6 Ž Vyšší odborné 0
7 M Vyučen/a 17
8 Ž Vyučen/a 8
9 M Základní 1
10 Ž Základní 5
a přidáme graf
> ggplot(fedu, aes(x=Var2, y=Freq, fill=Var1)) +
geom_bar(stat='identity', position=position_dodge()) +
geom_text(aes(label=Freq), hjust=1.6, color="white",position = position_dodge(0.9), size=3.5) +
coord_flip() +
xlab('Vzdělání') +
theme(axis.title.x = element_blank()) +
ggtitle('Dosažené vzdělání') +
labs(fill = 'Pohlaví')
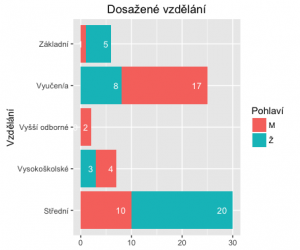
A co když budeme chtít jeden bar, ale rozdělený podle hodnot?
# seridime podle Var2 a Freq > library(plyr) > fedu_s <- arrange(fedu, Var2, Freq) > fedu_s Var1 Var2 Freq 1 M Střední 10 2 Ž Střední 20 3 Ž Vysokoškolské 3 4 M Vysokoškolské 4 5 Ž Vyšší odborné 0 6 M Vyšší odborné 2 7 Ž Vyučen/a 8 8 M Vyučen/a 17 9 M Základní 1 10 Ž Základní 5 # a pridame souhrnny soucet, rozdeleny s kazdym jinym Var2 > fedu_s_sum <- ddply(fedu_s, 'Var2', transform, label_ypos=cumsum(Freq)) > fedu_s_sum Var1 Var2 Freq label_ypos 1 M Střední 10 10 2 Ž Střední 20 30 3 Ž Vysokoškolské 3 3 4 M Vysokoškolské 4 7 5 Ž Vyšší odborné 0 0 6 M Vyšší odborné 2 2 7 Ž Vyučen/a 8 8 8 M Vyučen/a 17 25 9 M Základní 1 1 10 Ž Základní 5 6
A graf
ggplot(fedu_s_sum, aes(x=Var2, y=Freq, fill=Var1)) +
geom_bar(stat='identity') +
geom_text(aes(label=Freq, y=label_ypos), hjust=1.6, color="white", size=3.5) +
coord_flip() +
xlab('Vzdělání') +
theme(axis.title.x = element_blank()) +
ggtitle('Dosažené vzdělání') +
labs(fill = 'Pohlaví')
STM32F4Discovery + eLua + OSX
I fixed few bugs when compiling elua from git on osx – clone my branch clone official repo here.
$ ./build_elua.lua board=stm32f4discovery
create .bin file
$ arm-none-eabi-objcopy -O binary elua_lua_stm32f4discovery.elf elua_lua_stm32f4discovery.bin
create openocd config file for stm32f4 board:
$ cat ~/stm32f4discovery.cfg # stm32f4discover board source [find interface/stlink-v2-1.cfg] transport select hla_swd source [find target/stm32f4x.cfg] reset_config srst_only
and upload to the board:
$ openocd -f ~/stm32f4discovery.cfg \ -c "init" \ -c "reset halt" \ -c "sleep 100" \ -c "wait_halt 2" -c "echo \"--- Writing elua_lua_stm32f4discovery.bin\"" \ -c "flash write_image erase elua_lua_stm32f4discovery.bin 0x08000000" \ -c "sleep 100" \ -c "echo \"--- Verifying\"" \ -c "verify_image elua_lua_stm32f4discovery.bin 0x08000000" \ -c "sleep 100" \ -c "echo \"--- Done\"" \ -c "resume" \ -c "shutdown" Open On-Chip Debugger 0.9.0 (2015-11-16-01:48) Licensed under GNU GPL v2 For bug reports, read http://openocd.org/doc/doxygen/bugs.html Info : The selected transport took over low-level target control. The results might differ compared to plain JTAG/SWD adapter speed: 2000 kHz adapter_nsrst_delay: 100 none separate srst_only separate srst_nogate srst_open_drain connect_deassert_srst Info : Unable to match requested speed 2000 kHz, using 1800 kHz Info : Unable to match requested speed 2000 kHz, using 1800 kHz Info : clock speed 1800 kHz Info : STLINK v2 JTAG v25 API v2 SWIM v14 VID 0x0483 PID 0x374B Info : using stlink api v2 Info : Target voltage: 2.884520 Info : stm32f4x.cpu: hardware has 6 breakpoints, 4 watchpoints target state: halted target halted due to debug-request, current mode: Thread xPSR: 0x01000000 pc: 0x080063f0 msp: 0x20000c78 --- Writing elua_lua_stm32f4discovery.bin auto erase enabled Info : device id = 0x10076413 Info : flash size = 1024kbytes wrote 262144 bytes from file elua_lua_stm32f4discovery.bin in 7.783807s (32.889 KiB/s) --- Verifying target state: halted target halted due to breakpoint, current mode: Thread xPSR: 0x61000000 pc: 0x2000002e msp: 0x20000c78 verified 220776 bytes in 2.229936s (96.685 KiB/s) --- Done shutdown command invoked
Now you can connect to the board using /dev/tty.usbmodem621, 115200/8/n/1. You should get this prompt:
eLua# eLua# help Shell commands: help - shell help lua - start a Lua session ls - lists files and directories dir - lists files and directories cat - list the contents of a file type - list the contents of a file recv - receive files via XMODEM cp - copy files mv - move/rename files rm - remove files ver - show version information mkdir - create directories exit - exit the shell For more information use 'help <command>'. eLua# lua Press CTRL+Z to exit Lua Lua 5.1.4 Copyright (C) 1994-2011 Lua.org, PUC-Rio > print(pd.board() .. "/" .. pd.platform() .. "/" .. pd.cpu()) STM32F4DISCOVERY/STM32F4/STM32F407VG
enjoy :)
nodemcu – simple webserver
I’ve modified and updated this source:
local SSID = "my_wifi_ssid"
local SSID_PASSWORD = "my_wifi_password"
local function http_header(conn)
conn:send('HTTP/1.1 200 OK\n\n')
conn:send('<!DOCTYPE HTML>\n')
conn:send('<html>\n')
conn:send('<head><meta content="text/html; charset=utf-8">\n')
conn:send('<title>ESP8266 znouza test</title></head>\n')
end
local function connect (conn, data)
local query_data
conn:on ("receive",
function (cn, req_data)
query_data = get_http_req (req_data)
print (query_data["METHOD"] .. " " .. " " .. query_data["User-Agent"])
http_header(cn)
cn:send ("<body>")
cn:send ("<h1>Hello World from ESP8266 and NodeMCU!!</h1>")
cn:send ("</body></html>")
-- Close the connection for the request
cn:close ( )
end)
end
function wait_for_wifi_conn ( )
tmr.alarm (1, 1000, 1, function ( )
if wifi.sta.getip ( ) == nil then
print ("Waiting for Wifi connection")
else
tmr.stop (1)
print ("ESP8266 mode is: " .. wifi.getmode ( ))
print ("The module MAC address is: " .. wifi.sta.getmac ( ))
print ("Config done, IP is " .. wifi.sta.getip ( ))
end
end)
end
-- Build and return a table of the http request data
function get_http_req (instr)
local t = {}
local first = nil
local key, v, strt_ndx, end_ndx
for str in string.gmatch (instr, "([^\n]+)") do
-- First line in the method and path
if (first == nil) then
first = 1
strt_ndx, end_ndx = string.find (str, "([^ ]+)")
v = trim (string.sub (str, end_ndx + 2))
key = trim (string.sub (str, strt_ndx, end_ndx))
t["METHOD"] = key
t["REQUEST"] = v
else -- Process and remaining ":" fields
strt_ndx, end_ndx = string.find (str, "([^:]+)")
if (end_ndx ~= nil) then
v = trim (string.sub (str, end_ndx + 2))
key = trim (string.sub (str, strt_ndx, end_ndx))
t[key] = v
end
end
end
return t
end
-- String trim left and right
function trim (s)
return (s:gsub ("^%s*(.-)%s*$", "%1"))
end
-- Configure the ESP as a station (client)
wifi.setmode (wifi.STATION)
wifi.sta.config (SSID, SSID_PASSWORD,1)
-- Hang out until we get a wifi connection before the httpd server is started.
wait_for_wifi_conn ( )
-- Create the httpd server
svr = net.createServer (net.TCP, 30)
-- Server listening on port 80, call connect function if a request is received
svr:listen (80, connect)
nodemcu + el capitan
- download and install CH340g driver (check your FTDI chip)
- install CoolTerm (http://freeware.the-meiers.org/)
- install ESPlorer (http://esp8266.ru/esplorer/)
- open CoolTerm, options, choose appropriate /dev/cu.* port and connect
To flash
- download firmware
- Install esptool
git clone https://github.com/themadinventor/esptool.git cd esptool sudo python ./setup.py install
- upgrade firmware
$ python ./esptool.py --port=/dev/cu.wchusbserial620 write_flash -fm=dio -fs=32m 0x00000 /tmp/nodemcu_integer_0.9.6-dev_20150704.bin Connecting... Erasing flash... Took 3.92s to erase flash block Wrote 450560 bytes at 0x00000000 in 54.1 seconds (66.6 kbit/s)... Leaving...
eye killed?
Ever seen
$ eye load myconfig.eye Killed
If so, solution is quite simple. Run rm ~/.eye -rf and remove eye folder. Then re-run eye load and it should all work :)
Rubymotion – new bug found
I’m using this motion-addressbook in my project. Reported http://hipbyte.myjetbrains.com/youtrack/issue/RM-630
fixed in 2.37
= RubyMotion 2.37 =
* Fixed a regression where Dispatch.once did not work correctly when it was
invoked in some points.
* Fixed a bug where the compiler would crash with an assertion message
`[BUG] Object: SubtypeUntil ...' when compiling certain Ruby files.
* Fixed a bug in the compiler when compiling for ARM64 where certain types
would still be emitted with a 32-bit architecture in mind.
* Fixed a bug in the compiler when compiling for ARM64 where certain structs
would not be properly available (such as NSDecimal).
AWS S3 IAM user policy setup for bucket
First of all, setup your AWS account – and login into AWS Management Console. Then create any bucket you want.
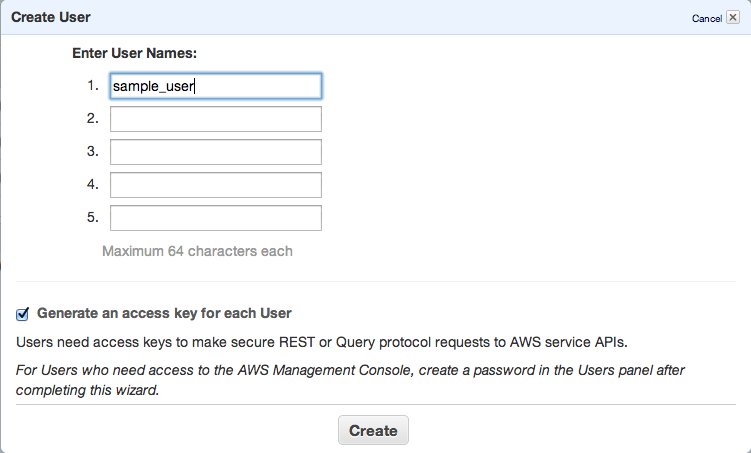
Next step is to add new IAM user – go to https://console.aws.amazon.com/iam/home?#users, select Users and click Create new user button.
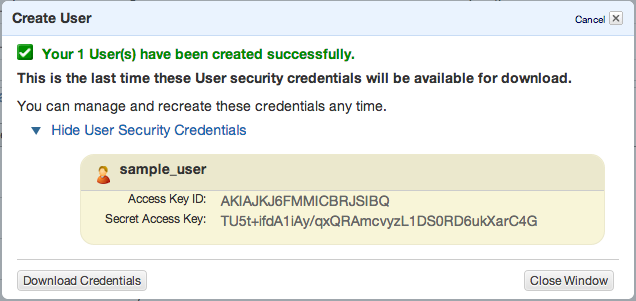
Click Create and copy/paste or download your access keys.
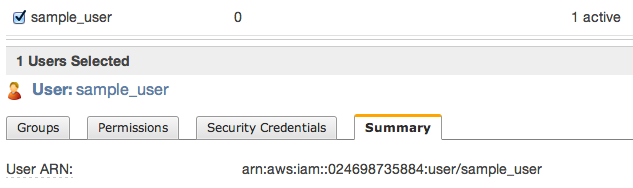
Then close window and click to summary tab – you’ll need to copy ARN notation of this user
s3cmd
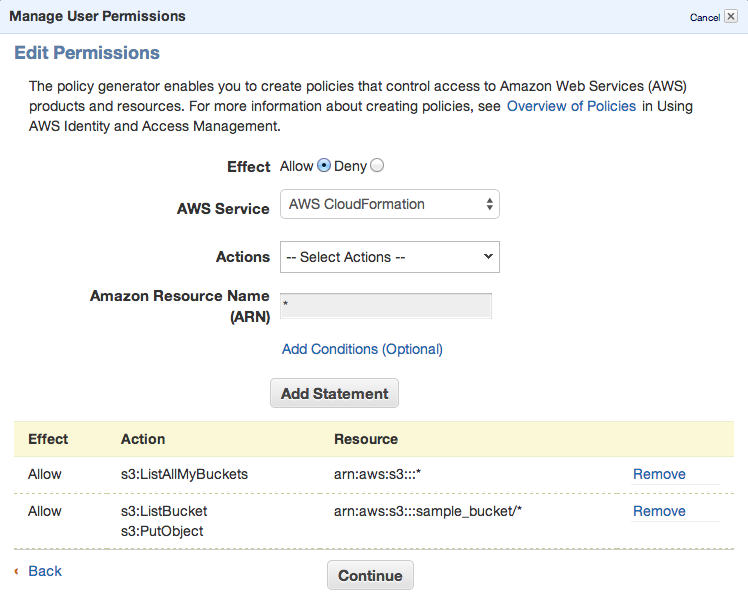
To be able to sync some folders and/or use s3cmd commandline tool, you need to setup some more policies. Click Permission tab and then Attach User Policy. Then choose Policy Generator and follow these steps:
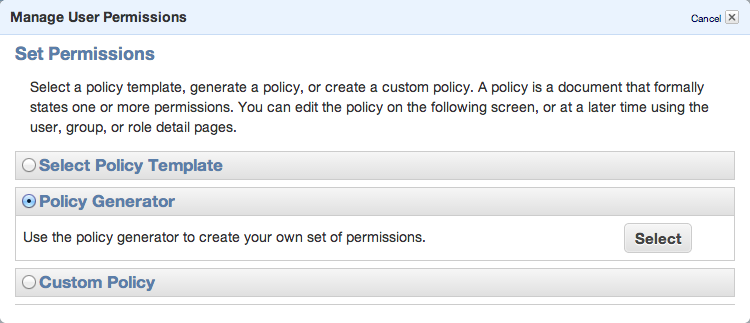 Set permissions as shown in following image – we need ListAllMyBuckets for :::* and ListBucket and PutObject for the one, specified bucket.
Set permissions as shown in following image – we need ListAllMyBuckets for :::* and ListBucket and PutObject for the one, specified bucket.
Click Continue and save new policy
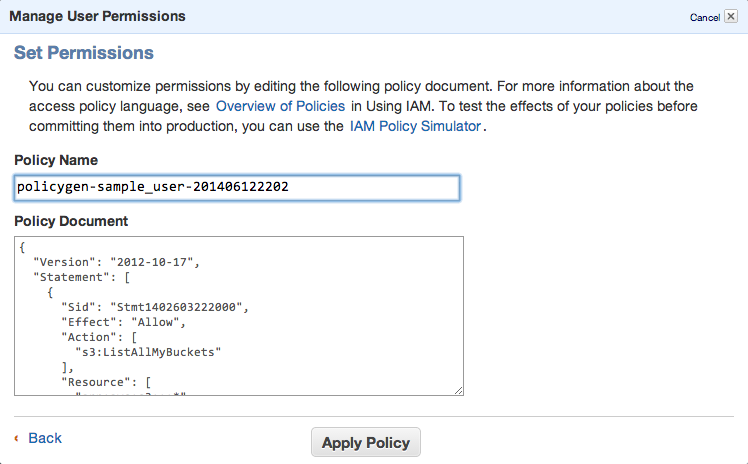
You can always edit the policy using Manage Policy. You should create this kind of policy file:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "Stmt1402603222000",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"s3:ListAllMyBuckets"
],
"Resource": [
"arn:aws:s3:::*"
]
},
{
"Sid": "Stmt1402603306000",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"s3:ListBucket",
"s3:PutObject"
],
"Resource": [
"arn:aws:s3:::sample_bucket/*"
]
}
]
}
That’s all. Lets move to bucket policy.
Bucket policy
Now you can open Policy Generator – http://awspolicygen.s3.amazonaws.com/policygen.html and start adding new items.
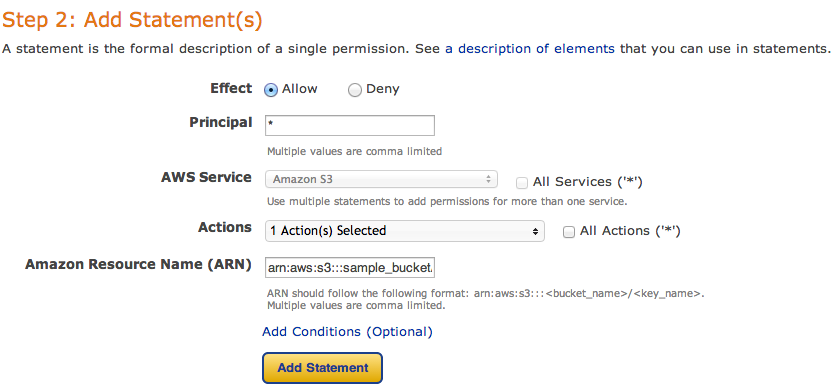
First of all, select your policy type – S3
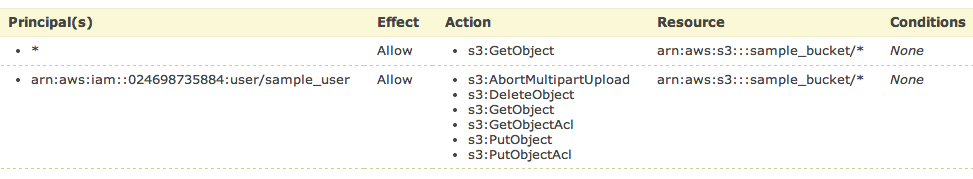
and then fill new policy – we need two policies – one for all users to read objects (GetObject) and second for your new user, to be able to upload, delete and get object as well.
and click Add Statement. The list below the form should look like
So, add your user the same way. As principal add your ARN notation (which you copied before) and add Actions as shown below.
All set. You need to click Generate Policy button and copy freshly generated JSON policy to your clipboard
{
"Id": "Policy1402594421281",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "Stmt1402593998750",
"Action": [
"s3:GetObject"
],
"Effect": "Allow",
"Resource": "arn:aws:s3:::sample_bucket/*",
"Principal": {
"AWS": [
"*"
]
}
},
{
"Sid": "Stmt1402594323930",
"Action": [
"s3:AbortMultipartUpload",
"s3:DeleteObject",
"s3:GetObject",
"s3:GetObjectAcl",
"s3:PutObject",
"s3:PutObjectAcl"
],
"Effect": "Allow",
"Resource": "arn:aws:s3:::sample_bucket/*",
"Principal": {
"AWS": [
"arn:aws:iam::024698735884:user/sample_user"
]
}
}
]
}
Last step is to add this policy to the bucket. Go back to your S3 console (https://console.aws.amazon.com/s3/home), click loupe icon next to bucket name and open Permission section. Click on Edit Bucket Policy and paste the generated policy into that window. Save and you’re done.
You’ll need API keys for use with Paperclip or any other S3 storage engine, so keep them safe.
PS: when you plan to use s3 as storage for your static files, avoid using underscore in your bucket name – as it does not comply with valid FQDN. ‘sample_bucket’ was used only as an example, in the real word you should use ‘sample-bucket’.
ATtiny13 – Hello World! :)
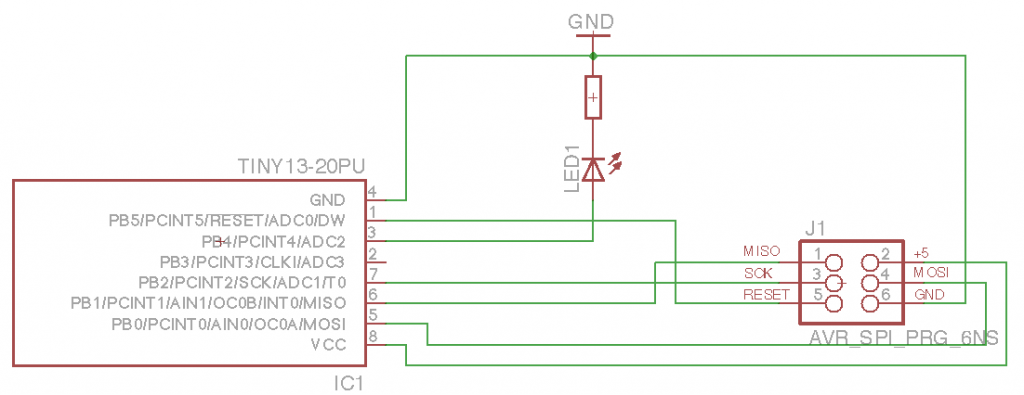
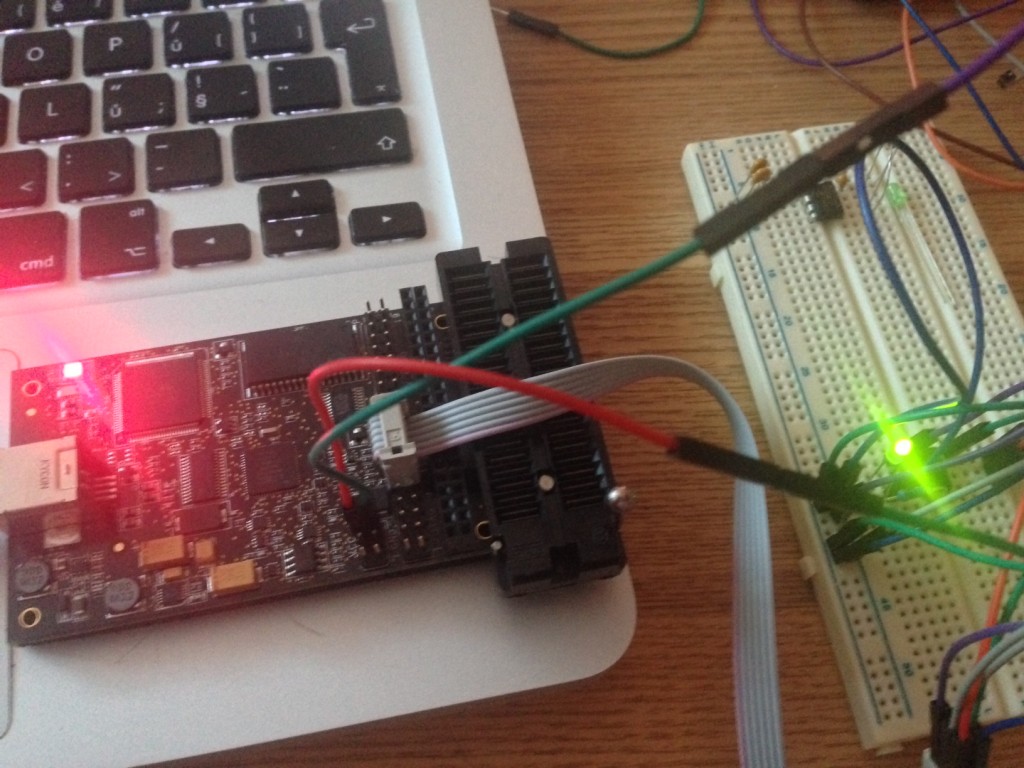
Finally managed to get into AVR programming. Using OSX, which I found as the worst platform for doing any kind of embed programming :( Sad. Anyway, there’s my first ATtiny schematics and code. I’m using AVR Dragon to flash code into the MCU.
The circuit is quite simple. I just confirm SPI flashing works and I’m able to turn the LED on. So here’s some code (using avr-gcc to compile and avrdure to upload). Create new project using avr-project and add this to main.c file:
#include <avr/io.h>
#include <util/delay.h>
int main(void)
{
const int msDelay = 50;
// PortB pin4 to output (set bit to 1 using SHL)
DDRB = 1<<DDB4;
// PortB to low
PORTB = 0;
while (1) {
// XOR on pin 4
PORTB ^= 1<<PB4;
_delay_ms(msDelay);
}
return 0;
}
Now we can compile the firmware and upload to our MCU.
$ make avr-gcc -Wall -Os -DF_CPU=8000000 -mmcu=attiny13 -c main.c -o main.o avr-gcc -Wall -Os -DF_CPU=8000000 -mmcu=attiny13 -o main.elf main.o rm -f main.hex avr-objcopy -j .text -j .data -O ihex main.elf main.hex avr-size --format=avr --mcu=attiny13 main.elf AVR Memory Usage ---------------- Device: attiny13 Program: 72 bytes (7.0% Full) (.text + .data + .bootloader) Data: 0 bytes (0.0% Full) (.data + .bss + .noinit)
No errors. Great. Connect AVR Dragon and upload our new firmware:
$ make flash
avrdude -c dragon_isp -P usb -p attiny13 -U flash:w:main.hex:i
avrdude: AVR device initialized and ready to accept instructions
Reading | ################################################## | 100% 0.15s
avrdude: Device signature = 0x1e9007
avrdude: NOTE: "flash" memory has been specified, an erase cycle will be performed
To disable this feature, specify the -D option.
avrdude: erasing chip
avrdude: reading input file "main.hex"
avrdude: writing flash (110 bytes):
Writing | ################################################## | 100% 0.46s
avrdude: 110 bytes of flash written
avrdude: verifying flash memory against main.hex:
avrdude: load data flash data from input file main.hex:
avrdude: input file main.hex contains 110 bytes
avrdude: reading on-chip flash data:
Reading | ################################################## | 100% 0.47s
avrdude: verifying ...
avrdude: 110 bytes of flash verified
avrdude: safemode: Fuses OK (H:FF, E:FF, L:6A)
avrdude done. Thank you.
For those, interested in .hex file – this is how it looks like:
$ cat main.hex :1000000009C00EC00DC00CC00BC00AC009C008C09A :1000100007C006C011241FBECFE9CDBF02D012C059 :10002000EFCF80E187BB18BA90E188B3892788BBFE :100030002FE738E381E0215030408040E1F700C0F5 :080040000000F3CFF894FFCF9C :00000001FF
and I made some commented assembler output (base is taken from avr-objdump -S main.elf).
cat main.S main.elf: file format elf32-avr Disassembly of section .text: 00000000 <__vectors>: 0: 09 c0 rjmp .+18 ; 0x14 <__ctors_end> 2: 0e c0 rjmp .+28 ; 0x20 <__bad_interrupt> 4: 0d c0 rjmp .+26 ; 0x20 <__bad_interrupt> 6: 0c c0 rjmp .+24 ; 0x20 <__bad_interrupt> 8: 0b c0 rjmp .+22 ; 0x20 <__bad_interrupt> a: 0a c0 rjmp .+20 ; 0x20 <__bad_interrupt> c: 09 c0 rjmp .+18 ; 0x20 <__bad_interrupt> e: 08 c0 rjmp .+16 ; 0x20 <__bad_interrupt> 10: 07 c0 rjmp .+14 ; 0x20 <__bad_interrupt> 12: 06 c0 rjmp .+12 ; 0x20 <__bad_interrupt> 00000014 <__ctors_end>: ; set stack to SRAM 14: 11 24 eor r1, r1 ; set 0 to r1 16: 1f be out 0x3f, r1 ; 0 -> SPH 18: cf e9 ldi r28, 0x9F ; RAMEND 1a: cd bf out 0x3d, r28 ; r28 -> SPL 1c: 02 d0 rcall .+4 ; call main loop at 0x22 1e: 12 c0 rjmp .+36 ; then call exit at 0x44 00000020 <__bad_interrupt>: 20: ef cf rjmp .-34 ; 0x0 <__vectors> 00000022 <main>: 22: 80 e1 ldi r24, 0x10 ; 1<<DDB4 (0x10) -> r24 24: 87 bb out 0x17, r24 ; set r24 -> DDRB 26: 18 ba out 0x18, r1 ; set r1 (0) -> PORTB 28: 90 e1 ldi r25, 0x10 ; 1<<DDB4 2a: 88 b3 in r24, 0x18 ; read PORTB -> r24 to XOR 2c: 89 27 eor r24, r25 ; XOR pin 4 2e: 88 bb out 0x18, r24 ; set r24 -> PORTB 30: 2f e7 ldi r18, 0x7F ; 0x01387f = wait 79999 ticks (50ms at 4MHz) 32: 38 e3 ldi r19, 0x38 ; 34: 81 e0 ldi r24, 0x01 ; 36: 21 50 subi r18, 0x01 ; decrease r18 by 1 38: 30 40 sbci r19, 0x00 ; and decrease other by carry bit 3a: 80 40 sbci r24, 0x00 ; 3c: e1 f7 brne .-8 ; repeat until zero set - jump to 0x36 3e: 00 c0 rjmp .+0 ; relative jump to 0x40 40: 00 00 nop ; do nothing 42: f3 cf rjmp .-26 ; jump back to 0x2a (loop) 00000044 <_exit>: 44: f8 94 cli 00000046 <__stop_program>: 46: ff cf rjmp .-2 ; 0x46 <__stop_program>